Choosing the right POS terminal is no longer a simple hardware decision—it’s a strategic business choice that can directly affect operational efficiency, customer experience, and long-term scalability. As digital payments, omnichannel retail, and data-driven decision-making become standard across industries, modern point-of-sale (POS) systems have evolved far beyond basic cash registers.
Whether you run a retail store, restaurant, hotel, or service-based business, selecting the right POS terminal requires a clear understanding of available types, core functionalities, and the tangible benefits each solution offers. A well-chosen POS terminal can streamline transactions, reduce errors, improve inventory management, and provide valuable insights into customer behavior.
This guide will walk you through how to choose a POS terminal, explaining different POS types, essential features, business benefits, and practical considerations—so you can make an informed, future-proof decision.
What Is a POS Terminal?
A POS terminal (Point of Sale terminal) is a system that enables businesses to process sales transactions. At its core, it handles payments, but modern POS terminals integrate hardware, software, and connectivity to manage sales, inventory, customer data, and reporting.
Core Components of a POS Terminal
- Hardware: Touchscreen display, card reader, receipt printer, barcode scanner
- Software: POS operating system, transaction management, reporting tools
- Payment Processing: Credit cards, debit cards, mobile wallets, QR payments
- Connectivity: Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Bluetooth, or cellular networks
Modern POS systems often function as centralized business management platforms rather than standalone devices.
Why Choosing the Right POS Terminal Matters
A poorly matched POS terminal can slow down operations, frustrate staff, and create friction for customers. On the other hand, the right POS solution enhances efficiency and supports business growth.
Key Business Impacts
- Faster checkout and reduced wait times
- Improved accuracy in transactions and reporting
- Better inventory visibility and control
- Enhanced customer experience
- Scalable infrastructure for future expansion
In competitive markets, POS performance can directly influence customer satisfaction and repeat business.
Types of POS Terminals
Understanding POS terminal types is the foundation of making the right choice. Each type serves different business models and operational needs.
1. Traditional Countertop POS Terminals
Countertop POS systems are fixed devices typically installed at checkout counters.
Best for:
- Retail stores
- Supermarkets
- Pharmacies
Key Characteristics:
- Stable power and internet connection
- Larger screens
- Integrated peripherals (printers, scanners)
Pros:
- Reliable and durable
- Handles high transaction volumes
Cons:
- Limited mobility
- Requires dedicated counter space
2. Mobile POS (mPOS) Terminals
Mobile POS terminals are compact, portable devices that connect via Wi-Fi or cellular networks.
Best for:
- Cafés and food trucks
- Pop-up stores
- On-the-go service providers
Key Characteristics:
- Lightweight and handheld
- Often tablet- or smartphone-based
Pros:
- Flexible and space-saving
- Faster service anywhere
Cons:
- Smaller screens
- Battery management required
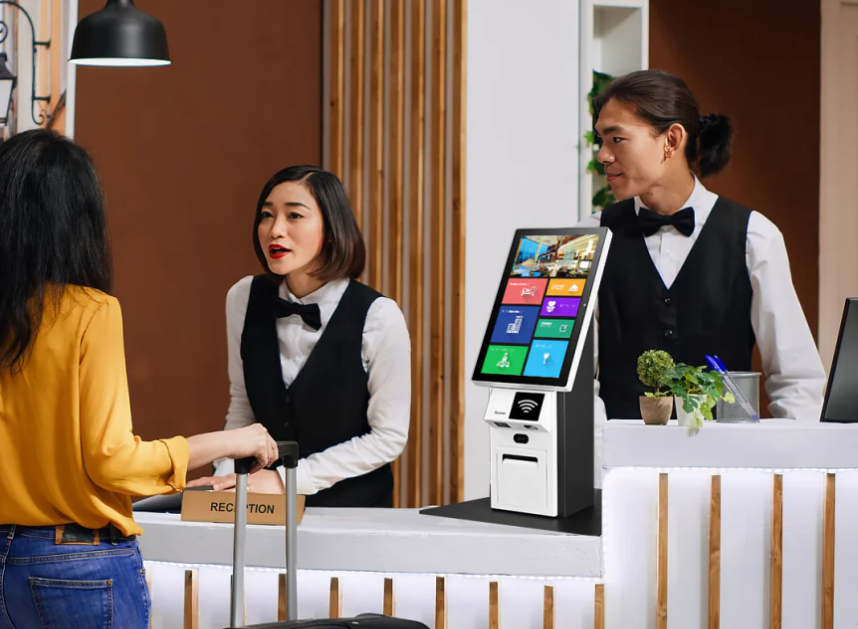
3. Smart POS Terminals
Smart POS terminals combine payment processing with Android-based applications and cloud connectivity.
Best for:
- Modern retail
- Hospitality
- Multi-location businesses
Key Characteristics:
- Touchscreen interface
- App-based ecosystem
- Cloud data sync
Pros:
- Highly customizable
- Supports advanced features
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost
- Requires software management
Many enterprises working with providers such as Elanda adopt smart POS terminals to balance flexibility with centralized management across locations.
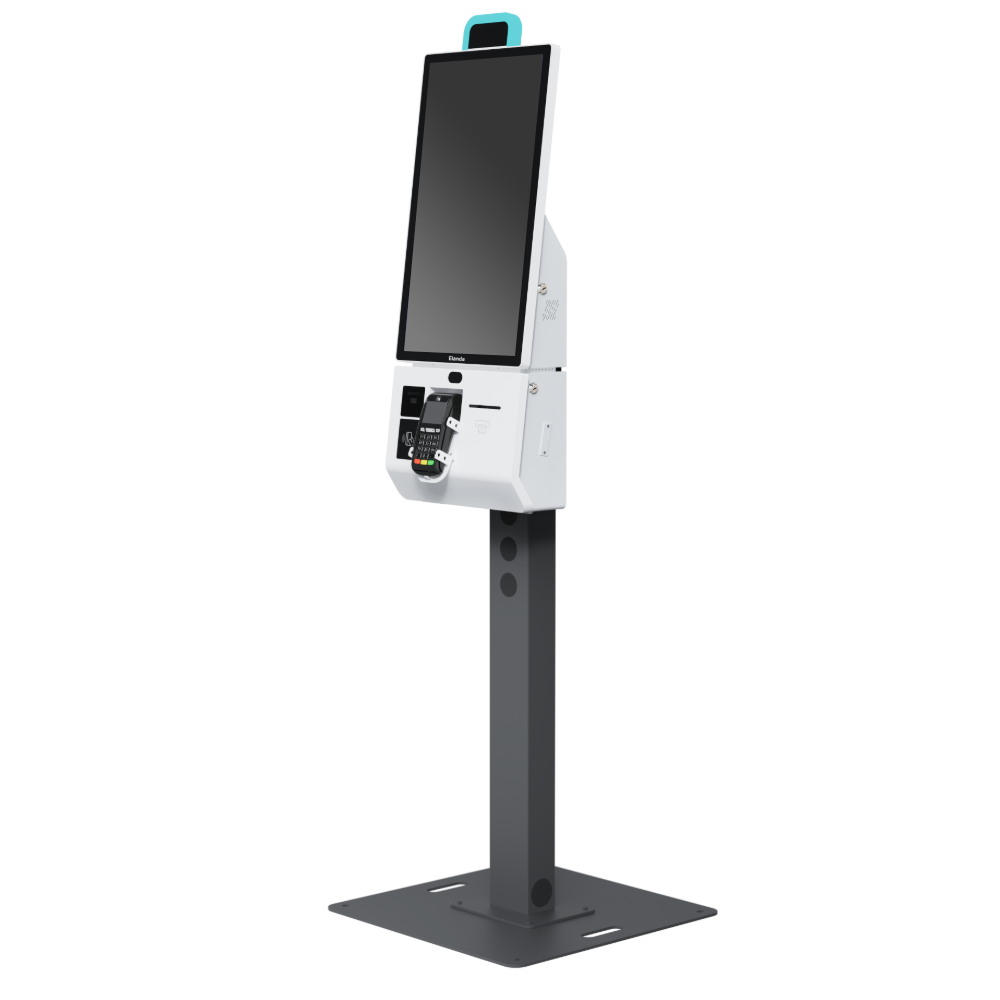
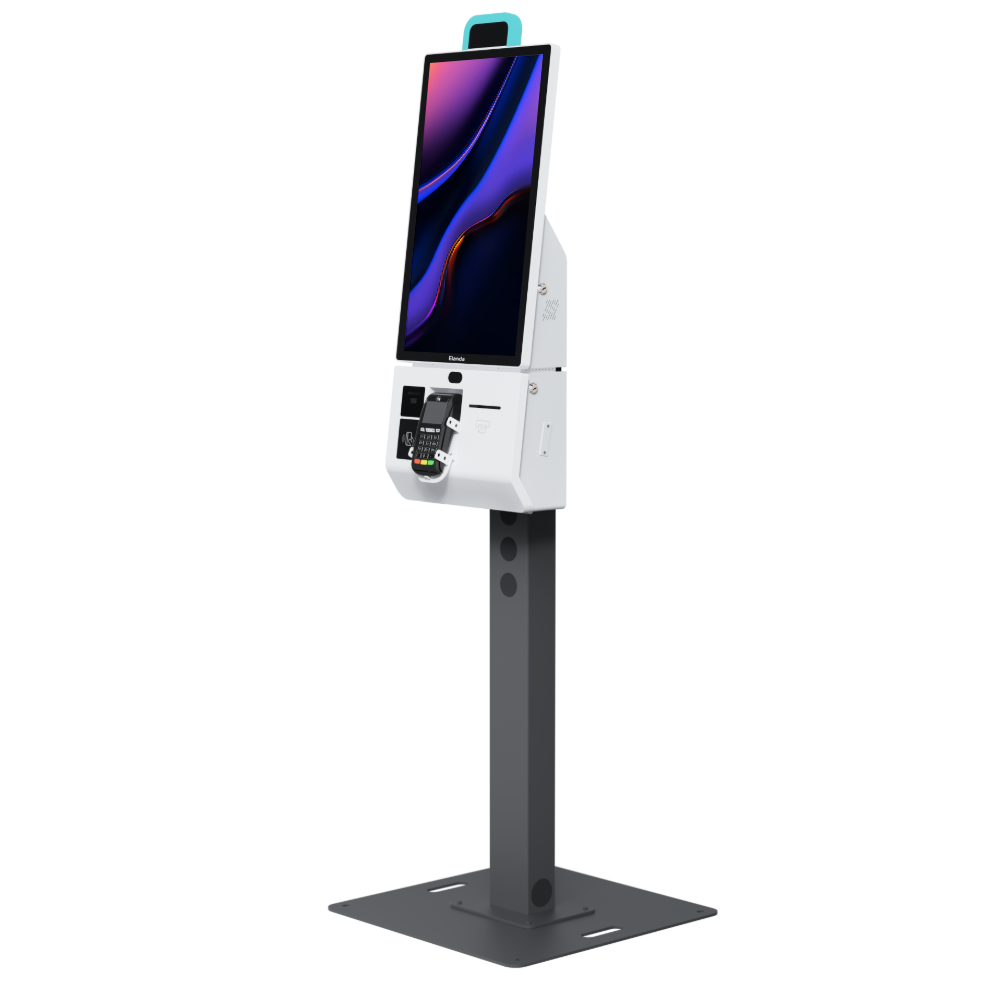
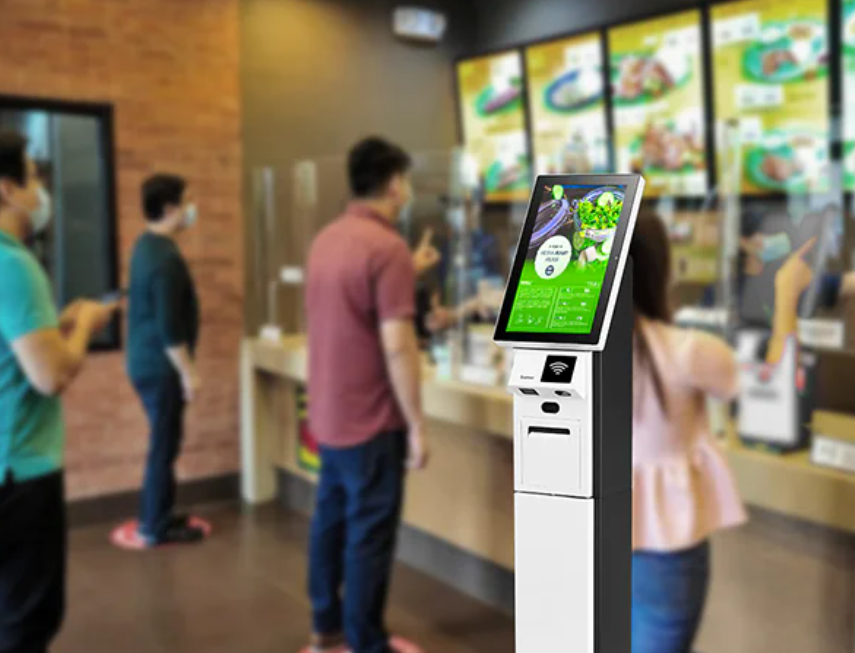
4. Self-Service POS Kiosks
Self-service POS kiosks allow customers to place orders and make payments independently.
Best for:
- Quick-service restaurants
- Cinemas
- Transportation hubs
Key Characteristics:
- Touchscreen ordering
- Integrated payment acceptance
Pros:
- Reduced labor costs
- Faster order processing
Cons:
- Higher initial investment
- Requires customer adoption
5. Cloud-Based POS Systems
Cloud POS systems store data remotely and enable real-time access from multiple devices.
Best for:
- Growing businesses
- Franchises
- Omnichannel retailers
Key Characteristics:
- Centralized data access
- Automatic updates
Pros:
- Remote management
- Easy scalability
Cons:
- Internet dependency
- Subscription-based pricing
Essential POS Terminal Functions
A POS terminal’s value lies in its functionality. Below are the most important features to evaluate.
Payment Processing Capabilities
A modern POS terminal should support multiple payment methods:
- Credit and debit cards
- Contactless payments (NFC)
- Mobile wallets (Apple Pay, Google Pay)
- QR code payments
- Cash handling (optional)
Payment flexibility improves customer convenience and reduces abandoned purchases.
Inventory Management
POS-integrated inventory tracking allows businesses to:
- Monitor stock levels in real time
- Set low-stock alerts
- Manage product variants
- Reduce overstock and shortages
This is especially critical for retail and hospitality operations.
Sales Reporting and Analytics
Robust POS reporting tools provide insights such as:
- Daily and monthly sales trends
- Best-selling products
- Peak business hours
- Staff performance metrics
Data-driven decisions lead to smarter pricing, staffing, and promotions.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Many POS systems now include CRM features:
- Customer profiles
- Purchase history
- Loyalty programs
- Personalized offers
These tools help build long-term customer relationships without complex external systems.
Multi-Location Management
For businesses operating across multiple locations, POS systems should enable:
- Centralized control
- Unified reporting
- Standardized pricing and menus
Providers like Elanda are often chosen for their ability to support consistent POS management at scale.
Security and Compliance
POS terminals must meet strict security standards:
- PCI DSS compliance
- Data encryption
- Secure user access controls
Strong security protects both business data and customer trust.
Key Benefits of Using the Right POS Terminal
Improved Operational Efficiency
Automated processes reduce manual work, minimize errors, and speed up transactions.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Faster checkout, flexible payments, and personalized service directly improve satisfaction.
Better Business Visibility
Real-time data access allows owners to respond quickly to trends and issues.
Scalability and Future Growth
The right POS terminal grows with your business—supporting new locations, products, and services without system replacement.

How to Choose the Right POS Terminal for Your Business
1. Understand Your Business Model
Different industries have different needs:
- Retail focuses on inventory and SKUs
- Restaurants need table and order management
- Service businesses prioritize mobility
2. Define Required Features
List must-have vs. nice-to-have features to avoid overpaying for unused functions.
3. Consider Total Cost of Ownership
Look beyond upfront hardware costs:
- Software subscriptions
- Payment processing fees
- Maintenance and upgrades
4. Evaluate Ease of Use
An intuitive interface reduces training time and staff errors.
5. Check Integration Capabilities
Ensure compatibility with accounting software, ERP systems, or e-commerce platforms.
6. Assess Vendor Reliability
Long-term support, updates, and technical assistance are critical for uninterrupted operations.

FAQs
1. What is the best POS terminal for small businesses?
The best POS terminal depends on business type. Small retailers often prefer cloud-based or mobile POS systems for flexibility and affordability.
2. Are POS terminals secure for card payments?
Yes, modern POS terminals use encryption and comply with PCI DSS standards to ensure secure transactions.
3. Can a POS terminal work without internet?
Some POS systems offer offline mode, storing transactions locally until connectivity is restored.
4. How long does it take to set up a POS terminal?
Setup can take from a few hours to several days, depending on system complexity and integrations.
5. Can one POS terminal support multiple stores?
Yes, cloud-based POS systems are designed for centralized multi-location management.
Conclusion
Choosing the right POS terminal is a strategic investment that shapes how your business operates today and scales tomorrow. By understanding the different POS types, evaluating essential functions, and aligning features with your business model, you can select a solution that enhances efficiency, improves customer experience, and delivers long-term value.
A well-chosen POS terminal is not just a payment device—it’s a powerful business management tool that supports smarter decisions, stronger customer relationships, and sustainable growth in an increasingly digital marketplace.